目录
背景
通过LINQ可以方便的查询并处理不同的数据源,使用Parallel LINQ (PLINQ)来充分获得并行化所带来的优势。
PLINQ不仅实现了完整的LINQ操作符,而且还添加了一些用于执行并行的操作符,与对应的LINQ相比,通过PLINQ可以获得明显的加速,但是具体的加速效果还要取决于具体的场景,不过在并行化的情况下一段会加速。
如果一个查询涉及到大量的计算和内存密集型操作,而且顺序并不重要,那么加速会非常明显,然而,如果顺序很重要,那么加速就会受到影响。
AsParallel() 启用查询的并行化
下面贴代码,看下效果,详情见注释:

class MRESDemo { /*code:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main() { ConcurrentQueue<Product> products = new ConcurrentQueue<Product>(); /*向集合中添加多条数据 可以修改数据量查看Linq和Plinq的性能*/ Parallel.For(0, 600000, (num) => { products.Enqueue(new Product() { Category = "Category" + num, Name = "Name" + num, SellPrice = num }); }); /*采用LINQ查询符合条件的数据*/ Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Restart(); var productListLinq = from product in products where (product.Name.Contains("1") && product.Name.Contains("2") && product.Category.Contains("1") && product.Category.Contains("2")) select product; Console.WriteLine("采用Linq 查询得出数量为:{0}", productListLinq.Count()); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("采用Linq 耗时:{0}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); /*采用PLINQ查询符合条件的数据*/ sw.Restart(); var productListPLinq = from product in products.AsParallel() /*AsParallel 试图利用运行时所有可用的逻辑内核,从而使运行的速度比串行的版本要快 但是需要注意开销所带来的性能损耗*/ where (product.Name.Contains("1") && product.Name.Contains("2") && product.Category.Contains("1") && product.Category.Contains("2")) select product; Console.WriteLine("采用PLinq 查询得出数量为:{0}", productListPLinq.Count()); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("采用PLinq 耗时:{0}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); Console.ReadLine(); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }

当前模拟的数据量比较少,数据量越多,采用并行化查询的效果越明显
AsOrdered()与orderby
AsOrdered:保留查询的结果按源序列排序,在并行查询中,多条数据会被分在多个区域中进行查询,查询后再将多个区的数据结果合并到一个结果集中并按源序列顺序返回。
orderby:将返回的结果集按指定顺序进行排序
下面贴代码方便大家理解:

class MRESDemo { /*code:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main() { ConcurrentQueue<string> products = new ConcurrentQueue<string>(); products.Enqueue("E"); products.Enqueue("F"); products.Enqueue("B"); products.Enqueue("G"); products.Enqueue("A"); products.Enqueue("C"); products.Enqueue("SS"); products.Enqueue("D"); /*不采用并行化 其数据输出结果 不做任何处理 */ var productListLinq = from product in products where (product.Length == 1) select product; string appendStr = string.Empty; foreach (string str in productListLinq) { appendStr += str + " "; } Console.WriteLine("不采用并行化 输出:{0}", appendStr); /*不采用任何排序策略 其数据输出结果 是直接将分区数据结果合并起来 不做任何处理 */ var productListPLinq = from product in products.AsParallel() where (product.Length == 1) select product; appendStr = string.Empty; foreach (string str in productListPLinq) { appendStr += str + " "; } Console.WriteLine("不采用AsOrdered 输出:{0}", appendStr); /*采用 AsOrdered 排序策略 其数据输出结果 是直接将分区数据结果合并起来 并按原始数据顺序排序*/ var productListPLinq1 = from product in products.AsParallel().AsOrdered() where (product.Length == 1) select product; appendStr = string.Empty; foreach (string str in productListPLinq1) { appendStr += str + " "; } Console.WriteLine("采用AsOrdered 输出:{0}", appendStr); /*采用 orderby 排序策略 其数据输出结果 是直接将分区数据结果合并起来 并按orderby要求进行排序*/ var productListPLinq2 = from product in products.AsParallel() where (product.Length == 1) orderby product select product; appendStr = string.Empty; foreach (string str in productListPLinq2) { appendStr += str + " "; } Console.WriteLine("采用orderby 输出:{0}", appendStr); Console.ReadLine(); } }
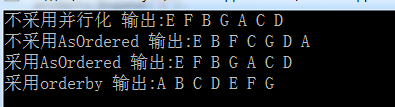
在PLINQ查询中,AsOrdered()和orderby子句都会降低运行速度,所以如果顺序并不是必须的,那么在请求特定顺序的结果之前,将加速效果与串行执行的性能进行比较是非常重要的。
指定执行模式 WithExecutionMode
对串行化代码进行并行化,会带来一定的额外开销,Plinq查询执行并行化也是如此,在默认情况下,执行PLINQ查询的时候,.NET机制会尽量避免高开销的并行化算法,这些算法有可能会将执行的性能降低到地狱串行执行的性能。
.NET会根据查询的形态做出决策,并不开了数据集大小和委托执行的时间,不过也可以强制并行执行,而不用考虑执行引擎分析的结果,可以调用WithExecutionMode方法来进行设置。、
下面贴代码,方便大家理解

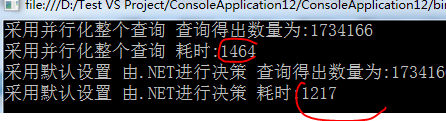
class MRESDemo { /*code:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main() { ConcurrentQueue<Product> products = new ConcurrentQueue<Product>(); /*向集合中添加多条数据*/ Parallel.For(0, 6000000, (num) => { products.Enqueue(new Product() { Category = "Category" + num, Name = "Name" + num, SellPrice = num }); }); /*采用并行化整个查询 查询符合条件的数据*/ Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Restart(); var productListLinq = from product in products.AsParallel().WithExecutionMode(ParallelExecutionMode.ForceParallelism) where (product.Name.Contains("1") && product.Name.Contains("2") && product.Category.Contains("1") && product.Category.Contains("2")) select product; Console.WriteLine("采用并行化整个查询 查询得出数量为:{0}", productListLinq.Count()); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("采用并行化整个查询 耗时:{0}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); /*采用默认设置 由.NET进行决策 查询符合条件的数据*/ sw.Restart(); var productListPLinq = from product in products.AsParallel().WithExecutionMode(ParallelExecutionMode.Default) where (product.Name.Contains("1") && product.Name.Contains("2") && product.Category.Contains("1") && product.Category.Contains("2")) select product; Console.WriteLine("采用默认设置 由.NET进行决策 查询得出数量为:{0}", productListPLinq.Count()); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("采用默认设置 由.NET进行决策 耗时:{0}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds); Console.ReadLine(); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
通过PLINQ执行归约操作
PLINQ可以简化对一个序列或者一个组中所有成员应用一个函数的过程,这个过程称之为归约操作,如在PLINQ查询中使用类似于Average,Max,Min,Sum之类的聚合函数就可以充分利用并行所带来好处。
并行执行的规约和串行执行的规约的执行结果可能会不同,因为在操作不能同时满足可交换和可传递的情况下产生摄入,在每次执行的时候,序列或组中的元素在不同并行任务中分布可能也会有区别,因而在这种操作的情况下可能会产生不同的最终结果,因此,一定要通过对于的串行版本来兴义原始的数据源,这样才能帮助PLINQ获得最优的执行结果。
下面贴代码:

class MRESDemo { /*code:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main() { ConcurrentQueue<int> products = new ConcurrentQueue<int>(); /*向集合中添加多条数据*/ Parallel.For(0, 6000000, (num) => { products.Enqueue(num); }); /*采用LINQ 返回 IEumerable<int>*/ var productListLinq = (from product in products select product).Average(); Console.WriteLine("采用Average计算平均值:{0}", productListLinq); /*采用PLINQ 返回 ParallelQuery<int>*/ var productListPLinq = (from product in products.AsParallel() select product).Average(); Console.WriteLine("采用Average计算平均值:{0}", productListPLinq); Console.ReadLine(); } }
如上述代码所示
在LINQ版本中,该方法会返回一个 IEumerable<int>,即调用 Eumerable.Range方法生成指定范围整数序列的结果,
在PLINQ版本中,该方法会返回一个 ParallelQuery<int>,即调用并行版本中System.Linq.ParallelEumerable的ParallelEumerable.Range方法,通过这种方法得到的结果序列也是并行序列,可以再PLINQ中并行运行。
如果想对特定数据源进行LINQ查询时,可以定义为 private IEquatable<int> products
如果想对特定数据源进行PLINQ查询时,可以定义为 private ParallelQuery<int> products
并发PLINQ任务

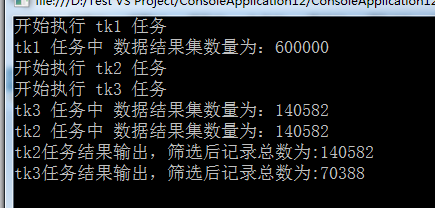
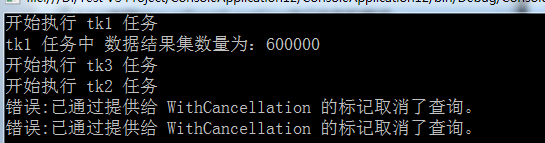
class MRESDemo { /*code:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main() { ConcurrentQueue<Product> products = new ConcurrentQueue<Product>(); /*向集合中添加多条数据*/ Parallel.For(0, 600000, (num) => { products.Enqueue(new Product() { Category = "Category" + num, Name = "Name" + num, SellPrice = num }); }); CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); /*创建tk1 任务 查询 符合 条件的数据*/ Task<ParallelQuery<Product>> tk1 = new Task<ParallelQuery<Product>>((ct) => { Console.WriteLine("开始执行 tk1 任务", products.Count); Console.WriteLine("tk1 任务中 数据结果集数量为:{0}", products.Count); var result = products.AsParallel().Where(p => p.Name.Contains("1") && p.Name.Contains("2")); return result; }, cts.Token); /*创建tk2 任务,在执行tk1任务完成 基于tk1的结果查询 符合 条件的数据*/ Task<ParallelQuery<Product>> tk2 = tk1.ContinueWith<ParallelQuery<Product>>((tk) => { Console.WriteLine("开始执行 tk2 任务", products.Count); Console.WriteLine("tk2 任务中 数据结果集数量为:{0}", tk.Result.Count()); var result = tk.Result.Where(p => p.Category.Contains("1") && p.Category.Contains("2")); return result; }, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion); /*创建tk3 任务,在执行tk1任务完成 基于tk1的结果查询 符合 条件的数据*/ Task<ParallelQuery<Product>> tk3 = tk1.ContinueWith<ParallelQuery<Product>>((tk) => { Console.WriteLine("开始执行 tk3 任务", products.Count); Console.WriteLine("tk3 任务中 数据结果集数量为:{0}", tk.Result.Count()); var result = tk.Result.Where(p => p.SellPrice > 1111 && p.SellPrice < 222222); return result; }, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion); tk1.Start(); Task.WaitAll(tk1, tk2, tk3); Console.WriteLine("tk2任务结果输出,筛选后记录总数为:{0}", tk2.Result.Count()); Console.WriteLine("tk3任务结果输出,筛选后记录总数为:{0}", tk3.Result.Count()); tk1.Dispose(); tk2.Dispose(); tk3.Dispose(); cts.Dispose(); Console.ReadLine(); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
如代码所示tk1,tk2,tk3三个任务,tk2,tk3任务的运行需要基于tk1任务的结果,因此,参数中指定了TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion,通过这种方式,每个被串联的任务都会等待之前的任务完成之后才开始执行,tk2,tk3在tk1执行完成后,这两个任务的PLINQ查询可以并行运行,并将会可能地使用多个逻辑内核。
取消PLINQ WithCancellation
通过WithCancellation取消当前PLINQ正在执行的查询操作,代码如下:

class MRESDemo { /*code:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main() { ConcurrentQueue<Product> products = new ConcurrentQueue<Product>(); /*向集合中添加多条数据*/ Parallel.For(0, 600000, (num) => { products.Enqueue(new Product() { Category = "Category" + num, Name = "Name" + num, SellPrice = num }); }); CancellationTokenSource cts = new CancellationTokenSource(); CancellationToken token = cts.Token; /*创建tk1 任务 查询 符合 条件的数据*/ Task<ParallelQuery<Product>> tk1 = new Task<ParallelQuery<Product>>((ct) => { var result = products.AsParallel(); try { Console.WriteLine("开始执行 tk1 任务", products.Count); Console.WriteLine("tk1 任务中 数据结果集数量为:{0}", products.Count); result = products.AsParallel().WithCancellation(token).Where(p => p.Name.Contains("1") && p.Name.Contains("2")); } catch (AggregateException ex) { foreach (Exception e in ex.InnerExceptions) { Console.WriteLine("tk3 错误:{0}", e.Message); } } return result; }, cts.Token); /*创建tk2 任务,在执行tk1任务完成 基于tk1的结果查询 符合 条件的数据*/ Task<ParallelQuery<Product>> tk2 = tk1.ContinueWith<ParallelQuery<Product>>((tk) => { var result = tk.Result; try { Console.WriteLine("开始执行 tk2 任务", products.Count); Console.WriteLine("tk2 任务中 数据结果集数量为:{0}", tk.Result.Count()); result = tk.Result.WithCancellation(token).Where(p => p.Category.Contains("1") && p.Category.Contains("2")); } catch (AggregateException ex) { foreach (Exception e in ex.InnerExceptions) { Console.WriteLine("tk3 错误:{0}", e.Message); } } return result; }, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion); /*创建tk3 任务,在执行tk1任务完成 基于tk1的结果查询 符合 条件的数据*/ Task<ParallelQuery<Product>> tk3 = tk1.ContinueWith<ParallelQuery<Product>>((tk) => { var result = tk.Result; try { Console.WriteLine("开始执行 tk3 任务", products.Count); Console.WriteLine("tk3 任务中 数据结果集数量为:{0}", tk.Result.Count()); result = tk.Result.WithCancellation(token).Where(p => p.SellPrice > 1111 && p.SellPrice < 222222); } catch (AggregateException ex) { foreach (Exception e in ex.InnerExceptions) { Console.WriteLine("tk3 错误:{0}", e.Message); } } return result; }, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion); tk1.Start(); try { Thread.Sleep(10); cts.Cancel();//取消任务 Task.WaitAll(tk1, tk2, tk3); Console.WriteLine("tk2任务结果输出,筛选后记录总数为:{0}", tk2.Result.Count()); Console.WriteLine("tk3任务结果输出,筛选后记录总数为:{0}", tk3.Result.Count()); } catch (AggregateException ex) { foreach (Exception e in ex.InnerExceptions) { Console.WriteLine("错误:{0}", e.Message); } } tk1.Dispose(); tk2.Dispose(); tk3.Dispose(); cts.Dispose(); Console.ReadLine(); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
指定查询时所需的并行度 WithDegreeOfParallelism
默认情况下,PLINQ总是会试图利用所有的可用逻辑内核达到最佳性能,在程序中我们可以利用WithDegreeOfParallelism方法指定一个不同最大并行度。
下面贴代码:

/*tk1任务 采用所有可用处理器*/ result = products.AsParallel().WithCancellation(token).WithDegreeOfParallelism(Environment.ProcessorCount).Where(p => p.Name.Contains("1") && p.Name.Contains("2") && p.Category.Contains("1") && p.Category.Contains("2")); /*tk1任务 采用1个可用处理器*/ result = products.AsParallel().WithCancellation(token).WithDegreeOfParallelism(1).Where(p => p.Name.Contains("1") && p.Name.Contains("2") && p.Category.Contains("1") && p.Category.Contains("2"));
好处:如果计算机有8个可用的逻辑内核,PLINQ查询最多运行4个并发任务,这样可用使用Parallel.Invoke 加载多个带有不同并行度的PLINQ查询,有一些PLINQ查询的可扩展性有限,因此这些选项可用让您充分利用额外的内核。
使用ForAll 并行遍历结果
下面贴代码:

class MRESDemo { /*code:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main() { ConcurrentQueue<Product> products = new ConcurrentQueue<Product>(); /*向集合中添加多条数据*/ Parallel.For(0, 1000, (num) => { products.Enqueue(new Product() { Category = "Category" + num, Name = "Name" + num, SellPrice = num }); }); products.AsParallel().Where(P => P.Name.Contains("1") && P.Name.Contains("2") && P.Name.Contains("3")).ForAll(product => { Console.WriteLine("Name:{0}", product.Name); }); Console.ReadLine(); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }
ForAll是并行,foreach是串行,如果需要以特定的顺序处理数据,那么必须使用上述串行循环或方法。
WithMergeOptions
通过WithMergeOptions扩展方法提示PLINQ应该优先使用哪种方式合并并行结果片段,如下:

下面贴代码查看下差异:

class MRESDemo { /*code:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main() { Console.WriteLine("当前计算机处理器数:{0}", Environment.ProcessorCount); ConcurrentQueue<Product> products = new ConcurrentQueue<Product>(); /*向集合中添加多条数据*/ Parallel.For(0, 600000, (num) => { products.Enqueue(new Product() { Category = "Category" + num, Name = "Name" + num, SellPrice = num }); }); Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); Thread.Sleep(1000); sw.Restart(); int count = 0; Task tk1 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { var result = products.AsParallel().WithMergeOptions(ParallelMergeOptions.AutoBuffered).Where(p => p.Name.Contains("1") && p.Name.Contains("2") && p.Category.Contains("1") && p.Category.Contains("2")); count = result.Count(); }); Task.WaitAll(tk1); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("ParallelMergeOptions.AutoBuffered 耗时:{0},数量:{1}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds, count); sw.Restart(); int count1 = 0; Task tk2 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { var result = products.AsParallel().WithMergeOptions(ParallelMergeOptions.Default).Where(p => p.Name.Contains("1") && p.Name.Contains("2") && p.Category.Contains("1") && p.Category.Contains("2")); count1 = result.Count(); }); Task.WaitAll(tk2); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("ParallelMergeOptions.Default 耗时:{0},数量:{1}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds, count1); sw.Restart(); int count2 = 0; Task tk3 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { var result = products.AsParallel().WithMergeOptions(ParallelMergeOptions.FullyBuffered).Where(p => p.Name.Contains("1") && p.Name.Contains("2") && p.Category.Contains("1") && p.Category.Contains("2")); count2 = result.Count(); }); Task.WaitAll(tk3); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("ParallelMergeOptions.FullyBuffered 耗时:{0},数量:{1}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds, count2); sw.Restart(); int count3 = 0; Task tk4 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => { var result = products.AsParallel().WithMergeOptions(ParallelMergeOptions.NotBuffered).Where(p => p.Name.Contains("1") && p.Name.Contains("2") && p.Category.Contains("1") && p.Category.Contains("2")); count3 = result.Count(); }); Task.WaitAll(tk4); sw.Stop(); Console.WriteLine("ParallelMergeOptions.NotBuffered 耗时:{0},数量:{1}", sw.ElapsedMilliseconds, count3); tk4.Dispose(); tk3.Dispose(); tk2.Dispose(); tk1.Dispose(); Console.ReadLine(); } } class Product { public string Name { get; set; } public string Category { get; set; } public int SellPrice { get; set; } }

需要注意的是:每一个选项都有其优点和缺点,因此一定奥测量显示第一个结果的时间以及完成整个查询所需要的时间,这点很重要 。
使用PLINQ执行MapReduce算法 ILookup IGrouping
mapreduce ,也称为Map/reduce 或者Map&Reduce ,是一种非常流行的框架,能够充分利用并行化处理巨大的数据集,MapReduce的基本思想非常简单:将数据处理问题分解为以下两个独立且可以并行执行的操作:
映射(Map)-对数据源进行操作,为每一个数据项计算出一个键值对。运行的结果是一个键值对的集合,根据键进行分组。
规约(Reduce)-对映射操作产生的根据键进行分组的所有键值对进行操作,对每一个组执行归约操作,这个操作可以返回一个或多个值。
下面贴代码,方便大家理解,但是该案列所展示的并不是一个纯粹的MapReduce算法实现:

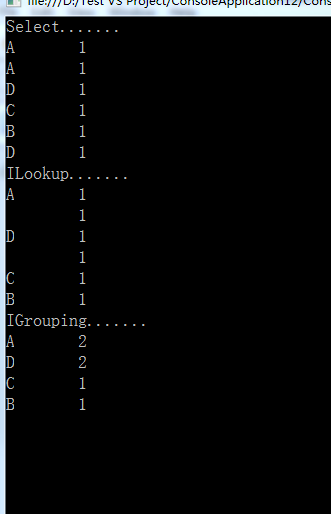
class MRESDemo { /*code:释迦苦僧*/ static void Main() { ConcurrentQueue<string> list = new ConcurrentQueue<string>(); list.Enqueue("A"); list.Enqueue("B"); list.Enqueue("C"); list.Enqueue("D"); list.Enqueue("A"); list.Enqueue("D"); Console.WriteLine("Select......."); list.AsParallel().Select(p => new { Name = p, Count = 1 }).ForAll((p) => { Console.WriteLine("{0}\t{1}", p.Name, p.Count); }); Console.WriteLine("ILookup......."); /*map操作生成的键值对由一个单词和数量1组成,该代码意在将每个单词作为键并将1作为值加入*/ ILookup<string, int> map = list.AsParallel().ToLookup(p => p, k => 1); foreach (var v in map) { Console.Write(v.Key); foreach (int val in v) Console.WriteLine("\t{0}", val); } /*reduce操作单词出现的次数*/ var reduce = from IGrouping<string, int> reduceM in map.AsQueryable() select new { key = reduceM.Key, count = reduceM.Count() }; Console.WriteLine("IGrouping......."); foreach (var v in reduce) { Console.Write(v.key); Console.WriteLine("\t{0}", v.count); } Console.ReadLine(); } }
关于PLINQ:声明式数据并行就写到这,主要是PLINQ下的查询注意项和查询调优的一些扩展方法。如有问题,欢迎指正。






